앙상블 모델 중 하나인 XG 부스트(eXtream Gradient Boosting)는 캐글 사용자에게 큰 인기를 얻고 있는 모델이다.
*앙상블: 여러 개의 학습 알고리즘을 사용해 더 좋은 성능을 얻는 방법
앙상블에는 배깅과 부스팅이 있다.
ensemble 종류 : single(CNN,RNN) bagging boosting
*배깅: 여러 개의 학습 알고리즘, 모델을 통해 각각 결과를 예측하고 모든 결과를 동등하게 보고 취합해서 결과를 얻는 방식
*부스팅: 배깅과 다르게 모델의 결과를 순차적으로 취합, 단순히 하나씩 취합하는 방법이 아니라 이전 알고리즘, 모델이
학습 후 잘못 예측한 부분에 가중치를 줘서 다시 모델로 가서 학습하는 방식
XG 부스트는 부스팅 기법 중 트리부스팅(Tree Boosting) 기법을 활용한 모델이다.
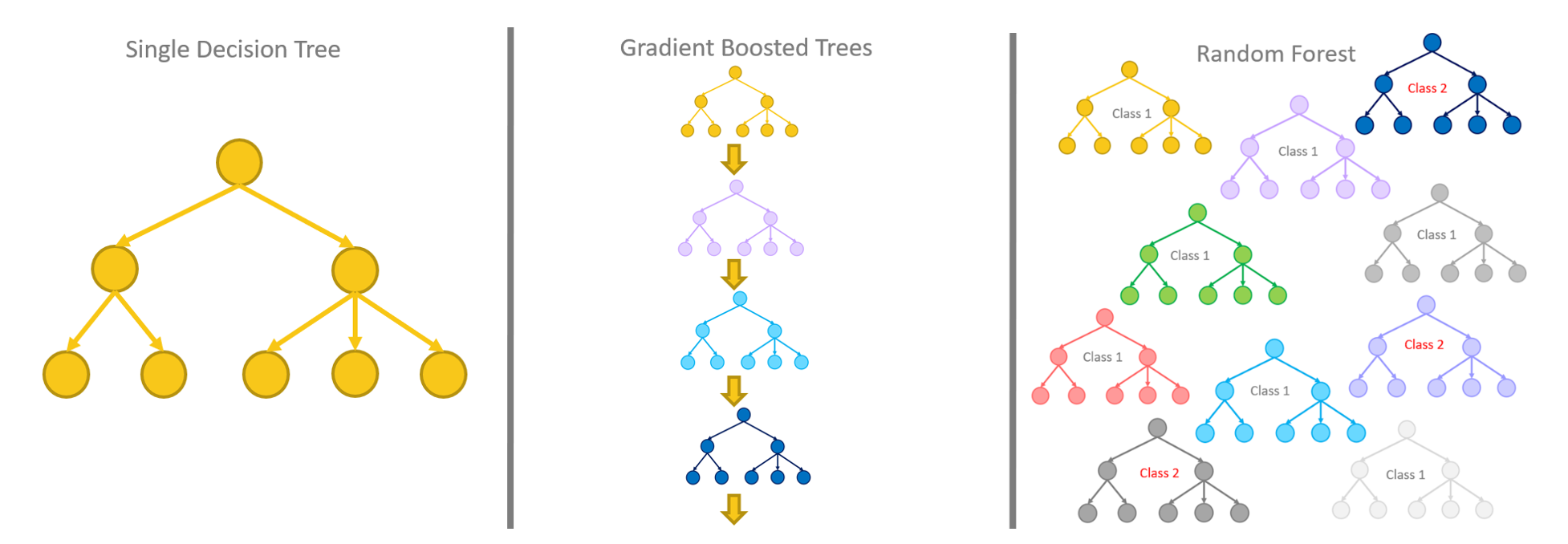
랜덤포레스트 모델이 여러 개의 의사 결정트리를 사영해 결과를 평균 내는 방법이라면, XGB는 동일한 원리를 적용해 여러개의 결과를 추천해 대신 오답에 대해 가중치를 부여했다. 가중치가 적용된 오답에 대해 가중치를 부여한다. 그리고 가중치가 적용된 오답에 대해서는 관심을 가지고 정답이 될 수 있도록 결과를 만들고 해당 결과에 대한 오답을 찾아 같은 작업을 반복한다.
최종적으로 XGB는 트리 부스팅 방식에 경사 하강법을 통해 최적화하는 방법이다. 또한 연산량을 줄이기 위해 병렬처리를 사용해 빠른 학습이 가능하다.
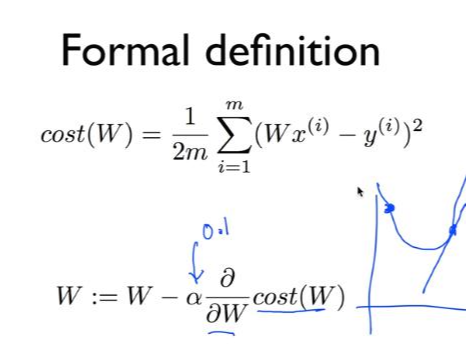
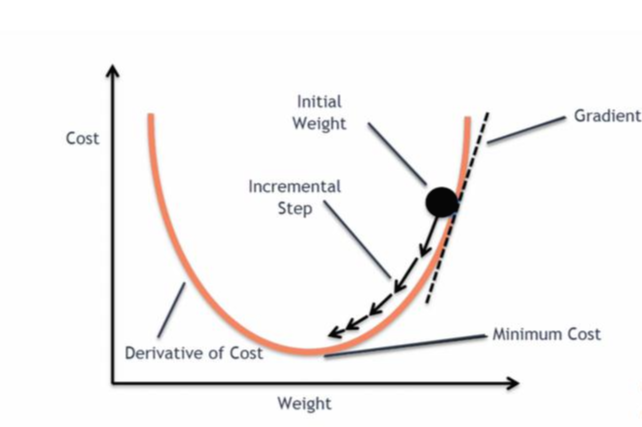
*경사하강법(Gradient descent): cost(W) = 1/mΣ|Wxi-yi|^2
cost값이 최소가 되는 지점을 미분을 통해 찾는다.
import xgboost as xgb
train_data = xgb.DMatrix(train_input.sum(axis=1),label=train_label) #XGB 형식 Matrix로 변환
eval_data = xgb.DMatrix(eval_input.sum(axis=1),label=eval_label)
data_list = [(train_data,'train'),(eval_data,'valid')]params = {}
params['objective'] = 'binary:logistic'
params['eval_metric'] = 'rmse'
bst = xgb.train(params,train_data,num_boost_round=1000,data_list,
early_stopping_rounds=10)# parameter
-
objective [default=reg:squarederror]
-
reg:squarederror: regression with squared loss.
-
reg:squaredlogerror: regression with squared log loss 12[log(pred+1)−log(label+1)]212[log(pred+1)−log(label+1)]2. All input labels are required to be greater than -1. Also, see metric rmsle for possible issue with this objective.
-
reg:logistic: logistic regression
-
reg:pseudohubererror: regression with Pseudo Huber loss, a twice differentiable alternative to absolute loss.
-
binary:logistic: logistic regression for binary classification, output probability
-
binary:logitraw: logistic regression for binary classification, output score before logistic transformation
-
binary:hinge: hinge loss for binary classification. This makes predictions of 0 or 1, rather than producing probabilities.
-
count:poisson –poisson regression for count data, output mean of poisson distribution
-
max_delta_step is set to 0.7 by default in poisson regression (used to safeguard optimization)
-
-
survival:cox: Cox regression for right censored survival time data (negative values are considered right censored). Note that predictions are returned on the hazard ratio scale (i.e., as HR = exp(marginal_prediction) in the proportional hazard function h(t) = h0(t) * HR).
-
survival:aft: Accelerated failure time model for censored survival time data. See Survival Analysis with Accelerated Failure Time for details.
-
aft_loss_distribution: Probabilty Density Function used by survival:aft objective and aft-nloglik metric.
-
multi:softmax: set XGBoost to do multiclass classification using the softmax objective, you also need to set num_class(number of classes)
-
multi:softprob: same as softmax, but output a vector of ndata * nclass, which can be further reshaped to ndata * nclass matrix. The result contains predicted probability of each data point belonging to each class.
-
rank:pairwise: Use LambdaMART to perform pairwise ranking where the pairwise loss is minimized
-
rank:ndcg: Use LambdaMART to perform list-wise ranking where Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain (NDCG) is maximized
-
rank:map: Use LambdaMART to perform list-wise ranking where Mean Average Precision (MAP) is maximized
-
reg:gamma: gamma regression with log-link. Output is a mean of gamma distribution. It might be useful, e.g., for modeling insurance claims severity, or for any outcome that might be gamma-distributed.
-
reg:tweedie: Tweedie regression with log-link. It might be useful, e.g., for modeling total loss in insurance, or for any outcome that might be Tweedie-distributed.
-
eval_metric [default according to objective]
-
Evaluation metrics for validation data, a default metric will be assigned according to objective (rmse for regression, and logloss for classification, mean average precision for ranking)
-
User can add multiple evaluation metrics. Python users: remember to pass the metrics in as list of parameters pairs instead of map, so that latter eval_metric won’t override previous one
-
The choices are listed below:
-
rmse: root mean square error
-
rmsle: root mean square log error: 1N[log(pred+1)−log(label+1)]2−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−√1N[log(pred+1)−log(label+1)]2. Default metric of reg:squaredlogerror objective. This metric reduces errors generated by outliers in dataset. But because log function is employed, rmsle might output nan when prediction value is less than -1. See reg:squaredlogerror for other requirements.
-
mae: mean absolute error
-
mphe: mean Pseudo Huber error. Default metric of reg:pseudohubererror objective.
-
logloss: negative log-likelihood
-
error: Binary classification error rate. It is calculated as #(wrong cases)/#(all cases). For the predictions, the evaluation will regard the instances with prediction value larger than 0.5 as positive instances, and the others as negative instances.
-
error@t: a different than 0.5 binary classification threshold value could be specified by providing a numerical value through ‘t’.
-
merror: Multiclass classification error rate. It is calculated as #(wrong cases)/#(all cases).
-
mlogloss: Multiclass logloss.
-
auc: Area under the curve. Available for binary classification and learning-to-rank tasks.
-
aucpr: Area under the PR curve. Available for binary classification and learning-to-rank tasks.
-
ndcg@n, map@n: ‘n’ can be assigned as an integer to cut off the top positions in the lists for evaluation.
-
ndcg-, map-, ndcg@n-, map@n-: In XGBoost, NDCG and MAP will evaluate the score of a list without any positive samples as 1. By adding “-” in the evaluation metric XGBoost will evaluate these score as 0 to be consistent under some conditions.
-
poisson-nloglik: negative log-likelihood for Poisson regression
-
gamma-nloglik: negative log-likelihood for gamma regression
-
cox-nloglik: negative partial log-likelihood for Cox proportional hazards regression
-
gamma-deviance: residual deviance for gamma regression
-
tweedie-nloglik: negative log-likelihood for Tweedie regression (at a specified value of the tweedie_variance_power parameter)
-
aft-nloglik: Negative log likelihood of Accelerated Failure Time model. See Survival Analysis with Accelerated Failure Time for details.
-
interval-regression-accuracy: Fraction of data points whose predicted labels fall in the interval-censored labels. Only applicable for interval-censored data. See Survival Analysis with Accelerated Failure Time for details.
-
num_boot_round = 1000 -> epoch 수 1000
early_stopping_rounds = 10 -> 10 epoch 동안 에러값이 별로 줄지 않으면 조기에 멈춤
result :
[320] train-rmse:0.38445 valid-rmse:0.42042
[321] train-rmse:0.38431 valid-rmse:0.42039
[322] train-rmse:0.38430 valid-rmse:0.42039
[323] train-rmse:0.38428 valid-rmse:0.42039
[324] train-rmse:0.38421 valid-rmse:0.42040
[325] train-rmse:0.38406 valid-rmse:0.42040
[326] train-rmse:0.38404 valid-rmse:0.42041
[327] train-rmse:0.38399 valid-rmse:0.42040
[328] train-rmse:0.38393 valid-rmse:0.42041
[329] train-rmse:0.38390 valid-rmse:0.42041
[330] train-rmse:0.38377 valid-rmse:0.42042
[331] train-rmse:0.38362 valid-rmse:0.42041
test_data 동일 시행
'👾 Deep Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| VAE(Variational Autoencoder) (1) (0) | 2021.02.18 |
|---|---|
| nvidia-smi 옵션 (0) | 2021.02.16 |
| RNN을 이용한 이미지 생성(feat.MNIST) (0) | 2021.02.15 |
| [DL] GRU (gated recurrent unit) (0) | 2021.02.10 |
| activation 종류 (0) | 2021.02.10 |
